I've been looking forward to being able to tell you about this new part of AWS for quite a while. Perhaps I'm biased, but I do think that this is a pretty big deal! I think we've managed to balance power and ease of use in a nice tidy package that will make AWS even more approachable for developers wishing to build powerful and highly scalable web applications.
AWS Elastic Beanstalk will make it even easier for you to create, deploy, and operate web applications at any scale. You simply upload your code and we'll take care of the rest. We'll create and configure all of the AWS resources (Amazon EC2 instances, an Elastic Load Balancer, and an Auto Scaling Group) needed to run your application. Your application will be up and running on AWS within minutes.
Much like the beanstalk in the popular fairy tale, Elastic Beanstalk allows you to start at ground level and climb toward the sky. However, as you will soon see, the beanstalk is built using a number of existing AWS services, not from magic beans.
When you use Elastic Beanstalk, you get to focus on the more creative and enjoyable aspects of application design and development while we take care of your software stack and your infrastructure. We do this in a very flexible way so that you still have complete control of what goes on. You can still access the underlying AWS resources if you'd like.
It has been years (1.5 decades to tell the truth) since I have done any serious Java development (Java Beans and the Java Native Interface, anyone?). Despite this, I was able to get the Elastic Beanstalk sample application up and running in less than five minutes. The application was effectively in production and ready to scale to meet the challenges of a world-wide load. Not too much later I was able to successfully compile and deploy some code of my very own.
If you are familiar with the market segment that is often called PaaS (short for Platform as a Service) you might be thinking "Ok, so what? Other environments have been able to do this for some time now. What's so special about this?" Well, lots of things. Here's a quick summary:
- Elastic Beanstalk is built on top of the proven AWS infrastructure. It takes full advantage of Amazon EC2, Elastic Load Balancing, Amazon CloudWatch, Auto Scaling, and other AWS services. You get all of the economy and scalability of AWS in a form that's easier and quicker to deploy than ever before.
- With Elastic Beanstalk you can choose to gradually assert control over a number of aspects of your application. You can start by tuning a number of parameters (see my post on the Elastic Beanstalk Console for more information about this). You can choose the EC2 instance type that provides the optimal amount of RAM and CPU power for your application. You can log in to the EC2 instances to troubleshoot application issues, and you can even take the default Elastic Beanstalk AMI (Amazon Machine Image), customize it, and then configure Amazon Beanstalk to use it for your application. This gradual assertion of control extends all the way to "eleven" -- you can choose to move your application off of Elastic Beanstalk and manage the raw components yourself if you so choose.
- Elastic Beanstalk was designed to support multiple languages and application environments. We are already working with solution providers to make this happen.
- Each of your Elastic Beanstalk applications will be run on one or more EC2 instances that are provisioned just for your application. Applications running on Elastic Beanstalk have the same degree of security as those running on an EC2 instance that you launch yourself.
- You can build an application that makes use of Elastic Beanstalk along with other services that you deploy on EC2 without having to worry about network latency across a wide-area network. You can launch the services in the same Region as your Elastic Beanstalk application. The ability to efficiently access existing services running on EC2 instances gives you additional flexibility and even more architectural and implementation options.
You can choose to remain blissfully unaware of the infrastructure that hosts your application and I fully expect that many of our customers will choose to do so. I also expect some of our customers to delve beneath the surface. Some will dip their toes in, others will take a deep dive. Either one is fine, and both are fully supported. When and if you choose to do this, you won't be entering some mysterious zone stuffed with undocumented code. Instead, you'll find that the Elastic Beanstalk AMI is based on the Amazon Linux AMI running the Apache Web Server, Tomcat, and the Enterprise Edition of the Java platform, all running on top of publicly documented AWS services.
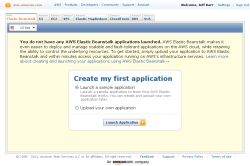 The public beta release of AWS Elastic Beanstalk allows you to write Java code, compile it, package it up into a WAR (web archive) file, and upload it to a Tomcat environment. You can do the upload using a new tab on the AWS Management Console; read my AWS Elastic Beanstalk From The AWS Management Console post to learn more.
The public beta release of AWS Elastic Beanstalk allows you to write Java code, compile it, package it up into a WAR (web archive) file, and upload it to a Tomcat environment. You can do the upload using a new tab on the AWS Management Console; read my AWS Elastic Beanstalk From The AWS Management Console post to learn more.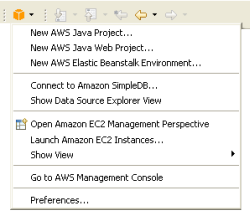 You can use the Elastic Beanstalk APIs and the Elastic Beanstalk command-line tools to connect your existing development tools and processes to Elastic Beanstalk. We've already used these APIs to extend the AWS Toolkit for Eclipse to allow developers to work with Elastic Beanstalk without needing to leave their IDE. See my post on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Eclipse Integration for additional information.
You can use the Elastic Beanstalk APIs and the Elastic Beanstalk command-line tools to connect your existing development tools and processes to Elastic Beanstalk. We've already used these APIs to extend the AWS Toolkit for Eclipse to allow developers to work with Elastic Beanstalk without needing to leave their IDE. See my post on AWS Elastic Beanstalk Eclipse Integration for additional information.
Comments
Post a Comment